AI reasoning models simulate human-like problem-solving, analyzing data and providing insights. To maximize their potential, it’s essential to craft effective prompts and avoid certain question types for better results.
Perfect Prompts for Reasoning Models
Reasoning models thrive when tasked with challenges that require complex thinking, analysis, and problem-solving. Crafting prompts that encourage these types of tasks will ensure you get thoughtful, useful responses. Here are several types of prompts that are ideal for reasoning models:
1. Problem-Solving Prompts
Reasoning models are especially adept at breaking down complex problems and offering structured solutions. When you give the AI a specific challenge, it can apply logical thinking to suggest solutions or generate new ideas.
Break down the process of creating a sustainable urban garden in a small apartment, considering space, resources, and plant compatibility.
This prompt allows the AI to apply logical thinking to generate structured, actionable solutions while considering real-world constraints. It encourages the model to think through a specific challenge and come up with practical ideas based on the factors involved.
2. Hypothesis Testing Prompts
Reasoning models can also test hypotheses, making them ideal for scenarios where you need to evaluate the potential outcomes of a situation based on various assumptions. The model can reason through the variables to come to a well-supported conclusion.
If a city starts offering free bike rentals during rush hour, how might different rental durations and locations impact the way people commute?
This prompt encourages the AI to evaluate how different variables, like rental duration and location, might influence a behavioral shift. The model can use logical thinking to assess how these factors interact, offering insights based on assumptions about human behavior and urban dynamics.
3. Comparative Analysis Prompts
Reasoning models excel at comparing two or more options and evaluating their pros and cons. These prompts allow the AI to consider multiple perspectives and make well-informed decisions.
Compare the pros and cons of using electric vehicles versus gasoline-powered vehicles in urban environments.
This prompt allows the AI to analyze two distinct options—electric vehicles and gasoline-powered vehicles—by weighing their advantages and disadvantages in the context of urban environments. It encourages the model to consider factors like environmental impact, cost, and practicality, leading to a comprehensive and balanced evaluation.
4. Strategic Planning Prompts
Strategic planning often involves evaluating long-term goals, available resources, and possible constraints. Asking a reasoning model to create a strategic plan can help generate innovative ideas and solutions.
Develop a five-year strategic plan for a local coffee shop to expand its customer base, considering staffing, marketing budget, and local competition.
This prompt challenges the AI to consider long-term growth objectives while factoring in resource limitations like staffing and budget. It invites the model to propose practical yet creative strategies that align with the coffee shop’s goals and constraints.
5. Counterfactual Thinking Prompts
Counterfactual reasoning, or “what if” scenarios, encourages the AI to explore alternative possibilities. These prompts invite the model to imagine different outcomes based on changes in variables, often yielding creative insights.
What would have happened if the internet was never invented? How would society and economies be different?
This prompt encourages the AI to think through alternate realities. It will need to use reasoning and logic to examine how various aspects of life—communication, business, and society—might have evolved without the internet.
6. Forecasting Prompts
Prompts that ask the AI to predict future trends or events based on current data and patterns help anticipate what may come. By analyzing existing trends, the AI can offer forecasts grounded in logical projections.
Based on current reading habits, predict how the popularity of physical books will change over the next decade.
This prompt allows the model to project potential shifts in reading media. It provides a logical, data-driven prediction based on current behaviors.
7. Risk Assessment Prompts
These prompts encourage the AI to assess potential risks and suggest ways to mitigate them. They focus on identifying vulnerabilities and offering strategies to minimize adverse outcomes.
Given the increasing risk of cyberattacks, what steps should companies take to strengthen their cybersecurity measures?
This prompt asks the AI to evaluate a specific risk and suggest practical steps for reducing that risk, utilizing logical analysis to provide actionable insights.
Don’t Bother With These Prompts
Despite their impressive capabilities, reasoning models can be thrown off track by prompts that lack clarity or logic. Certain types of questions won’t lead to useful or insightful responses. Here are some prompts you should avoid:
1. Vague or Open-Ended Prompts
Prompts that are too general or open-ended don’t provide enough direction for the AI to generate a focused response. Without a specific question or structure, the AI is likely to offer a vague, surface-level answer.
Tell me everything that lives in the Amazon Rainforest.
The sheer breadth of this prompt makes it difficult for the AI to provide a clear and concise answer. A more specific question, such as “What mammals live in the Amazon Rainforest?” or “Name the most common trees found in the Amazon Rainforest” would help generate a more focused and informative response.
2. Too Simple or Obvious Questions
Reasoning models are built to handle complexity. Asking overly simple questions won’t tap into their full potential and will lead to trivial, unhelpful answers.
This is a basic math problem that doesn’t require any reasoning. Simple arithmetic questions are better suited for calculators or basic AI tools, not sophisticated reasoning models.
3. Contradictory Prompts
When your prompt includes conflicting information or impossible scenarios, it can confuse the reasoning model. Contradictions hinder the AI’s ability to follow a logical path and can result in nonsensical answers.
What is the most efficient way to drive from point A to point B, considering the traffic but without using any roadways?
This prompt asks for a solution that contradicts itself (how can you drive without using roadways?). The reasoning model will either fail to answer or provide an irrelevant response.
4. Highly Subjective or Opinion-Based Prompts
Reasoning models rely on facts, logic, and data. When asked to provide purely subjective or opinion-based answers, they may struggle to offer a well-grounded response.
Which political party is the best for the country?
This type of question is inherently subjective and involves value judgments that the AI cannot make. The model is unable to form personal opinions, and a response could be biased or based on limited data.
5. Prompts with Insufficient Context
Reasoning models need sufficient context to generate meaningful answers. If a prompt doesn’t provide enough background or information, the AI might offer a superficial or irrelevant response.
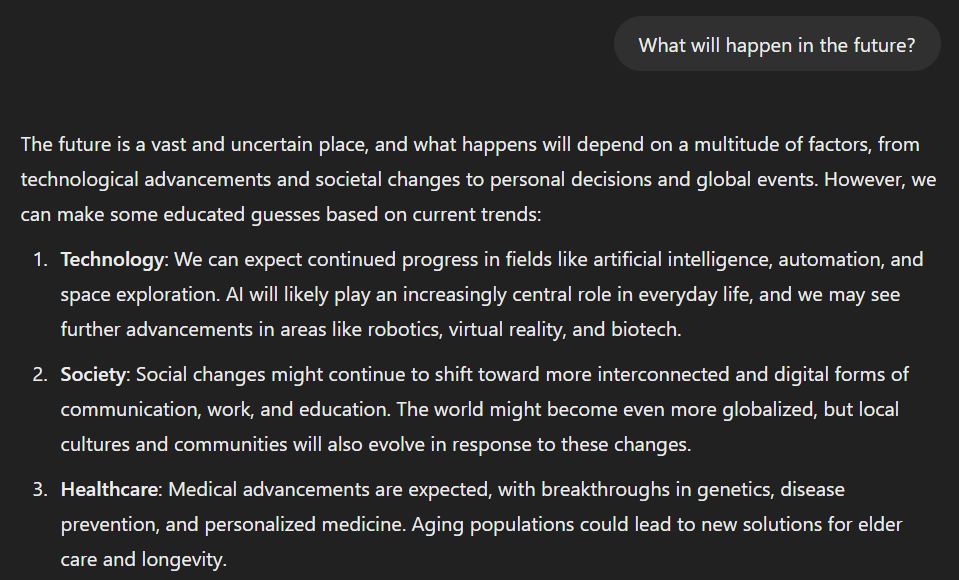
What will happen in the future?
This is an overly broad, open-ended question with no context. Without a defined scope, the AI is left guessing what kind of future scenarios you’re interested in, leading to a vague or generic answer.
6. Overly Complex or Ambiguous Prompts
Sometimes, asking overly complicated or unclear questions can overwhelm the AI and lead to incomplete or inaccurate answers. It’s important to strike a balance between complexity and clarity.
Explain how the advancement of artificial intelligence, changes in global supply chains, shifting consumer behaviors, and government regulations might affect the future of various industries over the next five years.
This prompt is too complex and combines too many broad topics without a clear focus. It’s difficult for the AI to process all the factors in a cohesive way. A more focused version like “How could advancements in AI impact the manufacturing industry over the next five years?” would yield a more structured and detailed response.
7. Prompts Lacking a Defined Purpose
When a prompt doesn’t have a clear intent or objective, the reasoning model struggles to understand the desired outcome, which results in vague or unhelpful responses.
Tell me about the economy.
This is too general, and without a clear focus, the AI cannot determine what specific aspect of the economy you’re interested in. A more targeted prompt, like “What are the causes of inflation in the current economy?” would be far more effective.
Related
How I Stop AI Chatbots From Agreeing With Me All the Time
Constant agreement isn’t intelligence.
Reasoning models are powerful tools, but to unlock their full potential, it’s crucial to ask clear, specific questions. Well-structured prompts lead to deeper insights, while vague or contradictory ones limit the quality of responses. By understanding which prompts work best, you can use reasoning models more effectively for analysis, strategy, and exploration.